According to Eurostat March 2018 report, almost 1 million foreigners obtain EU citizenship from the member states.
In 2016, around 995 000 persons acquired citizenship of a Member State of the European Union (EU), up from 841 000 in 2015 and 889 000 in 2014. The largest group acquiring citizenship of an EU Member State where they lived in 2016 was citizens of
- Morocco (101 300 persons, of whom 89% acquired citizenship of Spain, Italy or France),
- Albania (67 500, 97% acquired citizenship of Italy or Greece),
- India (41 700, almost 60% acquired British citizenship),
- Pakistan (32 900, more than half acquired British citizenship),
- Turkey (32 800, almost half acquired German citizenship),
- Romania (29 700, 44% acquired Italian citizenship)
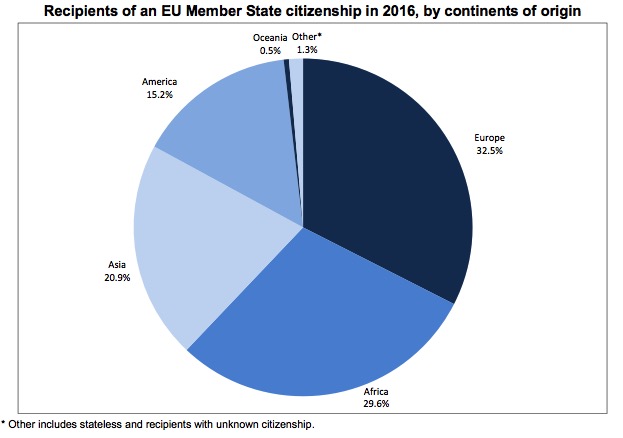
- Ukraine (24 000, 60% acquired citizenship ofGermany, Romania, Portugal or Italy).
- The number of UK nationals acquiring citizenship of another EU Member State more than doubled in 2016.
- The country with the highest naturalisation rate was Croatia (9.7 per hundred), followed by Sweden (7.9) and Portugal (6.5). The lowest naturalisation rates were found in Austria, Latvia and Slovakia (0.7).
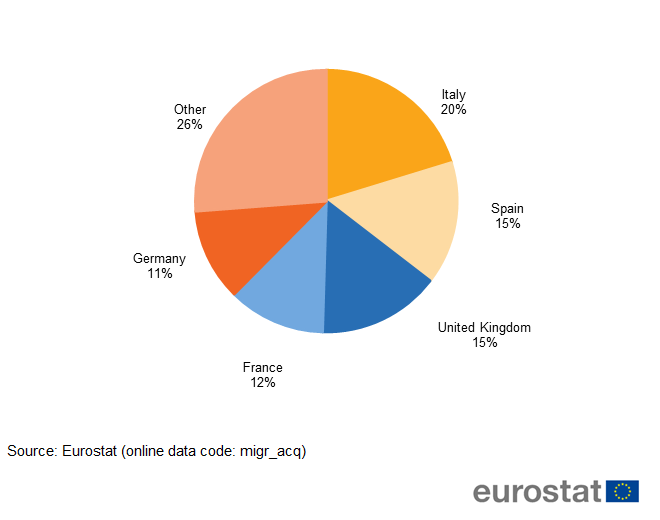
The top five citizenship-granting countries accounted for 74% of new citizenships granted in the EU in 2016:
- Italy (201 600 or 20 %),
- Spain (150 900 or 15 %),
- the United Kingdom (149 400 or 15 %),
- France (119 200 or 12 %) and
- Germany (112 800 or 11 %).
The European Union (EU) includes Belgium, Bulgaria, the Czech Republic, Denmark, Germany, Estonia, Ireland, Greece, Spain, France, Croatia, Italy, Cyprus, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Hungary, Malta, the Netherlands, Austria, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Slovenia, Slovakia, Finland, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
Citizenship is the legal bond between an individual and a state, acquired by birth, naturalisation or other means according to national legislation.
Naturalisation is the process by which a state grants its citizenship through a formal act on the application of the individual concerned. Other ways of granting citizenship may include spouses of nationals, minors adopted by nationals and descendants of nationals born abroad returning to the country of origin of their ancestors.
Source: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php/Acquisition_of_citizenship_statistics





