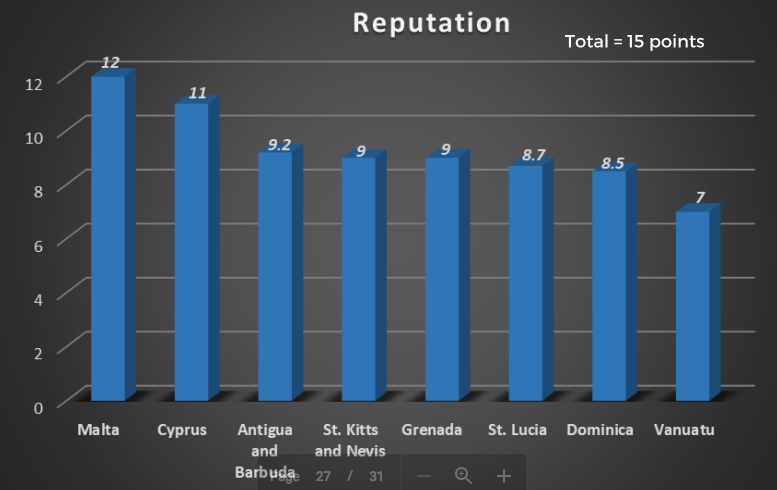
Malta ranks first for due diligence and compliance among all citizenship by investment programs, according to the new citizenship index published by HF Corporation.
Due diligence has been allocated seven points (7), while eight (8) points have been assigned to compliance. Out of total 15 points, Malta scored 12 points in first place followed by Cyprus at 11.
While each sovereign country has, and should have, the right to design its naturalisation policy – robust due-diligence standards, pricing befitting the offered benefits, smart processing and effective channeling of the foreign direct investment for the economic development of the countries and for the prosperity of their nations, by the recipient governments, will determine which programs will outperform in this competitive marketplace.
Reputation
Reputation of a program can be based on ‘due diligence’ and the ‘compliance’ of the country with the accepted international standards. Reputation of a program means how well the program is perceived, with an element of perception, in the outside world – that may include regulators, institutions, intergovernmental organisations and other professionals. The due diligence standards set by the responsible government agencies – either directly or through professional due diligence providers, are one way of reflecting the transparency of the program.
Due diligence
Due diligence standards are the standards opted by the governmental authority responsible for approval of the citizenship and naturalisation applications, in the respective countries, to ensure that persona non grata (unwanted persons) are not admitted under the respective program. These include, but are not limited to, running background checks on the applicants and the source of their funds and may either by run by the government agencies or through third-parties, or a combination of all these practices may be opted.
Compliance
Compliance of a country’s citizenship program with international standards, reflected somewhat but not wholly in its due diligence practices, is not always the same as the broader compliance of the country, itself, with the international standards including the financial standards.
Compliance of a particular country’s financial system with the international standards – which may not only be limited to differential tax rates – is something that also ensures that the nationals of that country will not have to face additional scrutiny in the outside financial
world.
While each sovereign country has, and should have, the right to design its naturalisation policy – robust due-diligence standards, pricing befitting the offered benefits, smart processing and effective channeling of the foreign direct investment for the economic development of the countries and for the prosperity of their nations, by the recipient governments, will determine which programs will outperform in this competitive marketplace
Methodology
Due diligence has been allocated seven points (7), while eight (8) points have been assigned to compliance. In order to determine compliance, policies announced by task forces, financial advisory bureaus, as well the regional organisations were taken into account.
It is important to analyse all these factors, side by side, as eventually these have a combined effect on the global reputation of a program. The stricter the due diligence standards and transparency, the better the long term reputation of a program; the more the compliance of a particular program with accepted standards, the greater the local, regional and global acceptance of the program – and hence, more foreign direct investment into the respective country – thereby more utilisation of ius pecuniae for the welfare of the indigenous population.
Read more about the report here





