A Sovereign wealth fund (SWF) is nothing but a state-owned investment fund that invests in real and financial assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, precious metals, or in alternative investments such as private equity fund or hedge funds. Sovereign wealth funds invest globally. Most SWFs are funded by revenues from commodity exports or from foreign-exchange reserves held by the central bank.
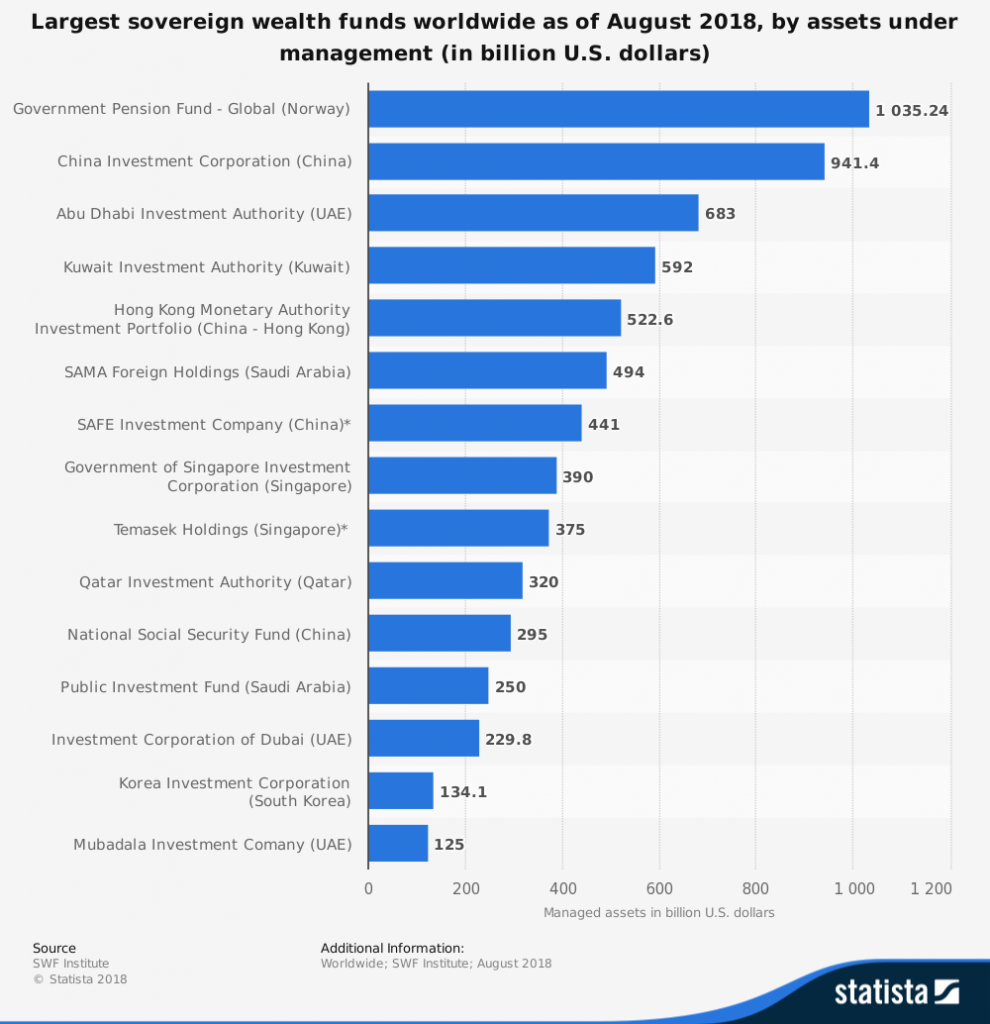
Norway has the biggest and largest SWF pension fund in the world with over $1 trillion of oil assets followed by China with close to $1 trillion in non-commodities. The term “sovereign wealth fund” was first used in 2005 by Andrew Rozanov in an article entitled, “Who holds the wealth of nations?” in the Central Banking Journal.
A Sovereign wealth fund (SWF) is pot of money, which is setup from a country’s CBI program, set aside for investment purposes to benefit the country’s economy and citizens.
Sovereign Fund of CBI programs
Citizenship by investment (CBI) programs have already helped create sovereign funds in several countries such as St Kitts, Antigua, Dominica, St Lucia and Grenada where in exchange for one time donation to the fund, citizenship for family can be acquired. Even Malta has one NDSF fund maintained with contributions from CBI program.
After the fall of its sugarcane industry, The St Kitts and Nevis Government established Sugar Industry Diversification Foundation (SIDF or the Foundation) was established on September 15, 2006, the foundation has invested over US$ 55,000,000.00 in the development of St. Kitts & Nevis by way of grants, loans and share holdings. Before 2017, a contribution of $250,000 to SIDF eligible to receive St Kitts citizenship. The Government after Hurricane season in 2017 cut the contribution to $150,000 establishing limited time Hurricane Relief Fund and later in 2018, Sustainable fund.
| Sovereign Fund | Contribution | |
| St Kitts and Nevis | Sustainable Growth Fund (SGF) | $150,000 |
| Antigua and Barbuda | National Development Fund (NDF) | $100,000 |
| Dominica | Economic Diversification Fund (EDF) | $100,000 |
| Saint Lucia | National Economic Fund (NEF) | $100,000 |
| Grenada | National Transformation Fund (NTF) | $150,000 |
| Malta | National Development & Social Fund (NDSF) | €650,000 |
The CBI funds and receipts can be held in SWF. For example the Dominica and Antigua used the national fund reserves to recover catastrophic damages from hurricane last year. Further the money was used for several purchases, rebuilding homes, hospitals, roads, airports and schools including social, employment and educational projects.
Malta citizenship revenues accumulated €432 million euros in NDSF fund under NDSF agency. The agency had awarded a grant of €950,000 to Mater Dei Hospital’s Cardiology Department to upgrade its two catheterisation suites benefited more than 3,000 patients a year . PM Muscat earlier this year announced, €50 million generated from the citizenship scheme will be spent on a massive social housing project that will create some 500 new units.
In 2018 Mauritius announced a citizenship program with $500K contributions to a sovereign fund.
According to ECCB, Establishing a regional Sovereign Wealth Fund (SWF) is a proactive step towards a sustainable long term economic strategy through CIPs.
- SWF which will become useful in insulating the economy when the inflows from the CBI are declining. For example St Kitts and Antigua revenues declined after losing visa waiver with Canada.
- Establish appropriate agency, with responsibility for regulation, compliance, to monitor the activities of the SWF to ensure that the managers adhere to the regulations.
- Legislation by Parliament to ensure that the SWF’s are transparent, financial statements are published and that the assets’ size and portfolios are known.
There are tremendous benefits to be had from creating SWFs, these include protecting the national wealth and economic diversification especially for small economies that depend on limited raw material exports. A sovereign wealth fund also contributes to a sustainable long term economic strategy and can aid central banks in sterilizing the surplus of liquidity, countering macroeconomic cycles and assist in sustaining key infrastructural projects.
The three main pillars of any SWF are the
- Legal framework on which it is built or developed,
- Institutional framework and the framework of its investment portfolio and
- Management of risk.
Sovereign Citizenship Fund in the Caribbean
A Sovereign Citizenship Fund (SCF) is just another sovereign wealth fund among countries operating CIPs where each country contributes a part of CBI revenues, form a administrative body, decide on investment portfolio and help one another.
To develop a SCF in the ECCU, member governments actively involved in economic citizenship programmes can provide a percentage of excess revenue to the Sovereign Citizenship Fund (SCF) on a monthly, quarterly or annual basis.
The Caribbean countries can decide to combine the allocations from the CBI, with a 1.0 per cent (or a percentage agreed on) of GDP. Countries without the CBI could have provisions to be included in the SCF.
- The Government of St Kitts and Nevis received $414.7m in non-tax revenue for 2014 of which $296.1m was attributed to the CBI. The budgeted amount for the CBI in 2014 was estimated at $100.0m. Presumably, the government of St Kitts and Nevis can allocate a portion of the excess $196.1m to a SWF for investment purposes. A conservative allocation of 15.0 to 20.0% can provide $29.4m to $39.2m to the fund.
- The Government of Saint Lucia projects average collections of approximately $70m per annum from its Citizenship by Investment Programme. An allocation of 15 to 20 per cent will contribute approximately $10.5m annually to a SWF.
- The Government of Antigua and Barbuda and Grenada have seen annual inflows of over $100m from the economic citizenship programme
- The government of Dominica budgeted on average $75m per fiscal year for the last 2 years. The conservative 15 to 20 per cent allocation towards an ECCU wide SWF could range from about $15m to $38m per annum on average from each country with a CBI programme.
These funds can yield favourable returns if invested using a 50/30/20 split in fixed income, equity and cash respectively. SWFs can also be designed to provide an additional cash flow stream to governments when it is absolutely necessary.
Sovereign Donation Fund
The countries offering CIP programs must setup a separate fund to accept small donations from CBI citizens for philanthropic work. This is separate and not a citizenship donation. Since most CBI citizens do not live in the country at all after receiving passport, it is not clear how many CBI citizens have made philanthropic donations to caribbean countries. The countries offering CIP must make an effort to collect such donations from CBI citizens and diaspora population. This fund can be used for education, elderly people care, free food medicine distribution and help displaced people etc..
For example, in Malta, IIP applicants coming from wealthy background have donated 550 donations to a total of €3.5 million euros for philanthropic purposes. This averages 6,363 euros per donation.
Biggest sovereign fund by country