CBI citizens are given CARICOM passport issued by the 15 member states of the Caribbean Community(CARICOM) for their citizens. All CBI citizens in the Caribbean are also CARICOM citizens
CARICOM nationals are entitled to the same rights as all other Community nationals, including the right of entry into other member states. At present only five of the fifteen CARICOM states currently offer CBI programmes: St. Kitts & Nevis, Grenada, Dominica, Antigua & Barbuda and St Lucia.
While most CBI citizens only think of visa free access to EU/UK, only few effectively make use of Caricom passport to freely travel to other caribbean countries for business and pleasure . CARICOM passport can be used both for intra-regional and international travel.
CARICOM
CBI citizens as CARICOM nationals enjoy free movement in CARICOM states. All CARICOM Nationals are entitled to free entry into another Member State, with an automatic six month stay.
CBI citizens cannot however cannot automatically do the following activities in CARICOM states without permission, which subjected to national laws
- stay indefinitely
- take up residence
- work without permission
- provide services
- establish a business
CBI citizens wishing to live and work in another CARICOM State indefinitely must obtain a CSME Skills Certificate which is available for several categories.
CBI beneficiaries would be considered Community Nationals for the purposes of the Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas and would be entitled to all the rights and benefits such nationals enjoy under the Revised Treaty, including the right to travel to, live and work in another member state, subject to exceptions.
Article 32(5) of the Revised Treaty of Chaguaramas defines a Community “national” as:
- A person shall be regarded as a national of a Member State if such person –
- Citizen of that State;
- Has a connection with that State of a kind which entitles him to be regarded as belonging to or, if it be so expressed, as being a native or resident of the State for the purposes of the laws thereof relating to immigration
Rights enjoyed by nationals
- Non-discrimination
- Rights of establishment and to work (non-wage earning activities)
- movement of capital by businesses and individuals.
- Cross border services
- Free movement and entry of people
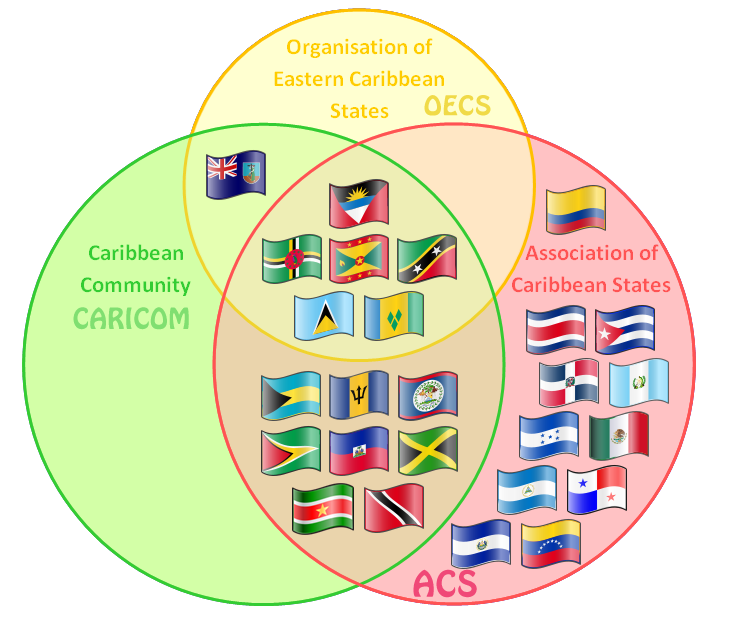
These are 15 full member states of the CARICOM community
| Name | Join date | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 4 July 1974 | ||
| 4 July 1983 | Not part of customs union | |
| 1 August 1973 | Founding member | |
| 1 May 1974 | ||
| 1 May 1974 | ||
| 1 May 1974 | ||
| 1 August 1973 | Founding member | |
| 2 July 2002 | Provisional membership on 4 July 1998 | |
| 1 August 1973 | Founding member | |
| 1 May 1974 | British overseas territory | |
| 26 July 1974 | ||
| 1 May 1974 | ||
| 1 May 1974 | ||
| 4 July 1995 | ||
| 1 August 1973 | Founding member |
Organization of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS)
Five out of six OECS countries currently offer CBI schemes creating economic citizens.
CBI citizens can live and work in OECS member states as a result of right of freedom of movement granted in Article 12 of the Protocol of the Eastern Caribbean Economic Union of the Revised Treaty of Basseterre.
Citizens of OECS member states can travel freely other member states with just an ID card (drivers license, passport etc)
The OECS has 7 founding members that enjoy full membership:
- Antigua and Barbuda,
- Commonwealth of Dominica,
- Grenada,
- Montserrat,
- Saint Kitts and Nevis,
- Saint Lucia,
- Saint Vincent and The Grenadines.